When you are building your dream home, you need to be more cautious about building safety and seismic protection. If you have no choice but to build in a seismic-prone area, you can include seismic dampers in buildings to reduce the risk of damage and destruction due to seismic events.
In this blog, we are going to understand the importance of seismic dampers, their different types, pros & cons and how to choose a suitable type for your house.
What are Seismic Dampers?
You can understand seismic dampers as special mechanical devices used in buildings to absorb the effects of seismic events or external impacts and protect structures, making them more stable. These seismic dampers will be used in both new construction and retrofit works. These dampers are often used in buildings that are constructed in earthquake-prone areas. These dampers will be attached to two points of the building to absorb the earthquake waves.
You can considerably reduce the impact and damage caused by seismic activity like earthquakes by installing these dampers along with other essential earthquake-resistant measures.
How do Seismic Dampers Work?
Seismic dampers absorb the seismic wave’s kinetic energy that penetrates a building structure. These dampers allow the building to move elastically and dissipate the earthquake’s energy. They function by allowing controlled movement of the building and converting the earthquake’s energy into heat or frictional force, which is then dissipated.
These dampers are usually used in place of structural elements like diagonal callipers to control all the seismic damage in the structure. This way, it partly absorbs the seismic energy, reducing the motion of buildings.
Types of Seismic Dampers Used in India
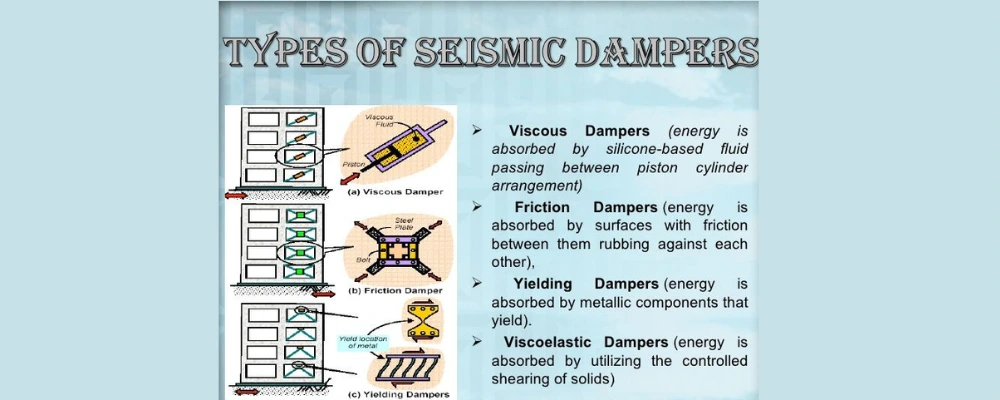
There are several types of dampers that effectively absorb and dissipate seismic energy. The main types include:
Viscous Dampers
These viscous dampers will be made with viscous fluid inside a cylinder/tank and placed along the length of an oil or gas pipeline. The heavy fluid inside the cylinder or tank will be undisturbed until it is subjected to a force. When an earthquake hits, the fluid moves from the cylinder’s one end to another and absorbs seismic energy from the building. These viscous dampers are easy to install and can be used for up to 30 years. You have the option to choose from their diversity of sizes.
They are effective in absorbing both minor and strong earthquake forces. Viscous dampers are commonly used in high-rise buildings and bridges.
This type of damper is connected to the building structure in three ways:
- Damper installation in the floor or foundation ( in case of seismic isolation)
- Linking dampers in stern pericardial braces
- Installation of damper in diagonal braces.
Although viscous dampers offer considerable advantages, the installation cost and maintenance charges are very high.
Friction Dampers
In friction dampers, the kinetic energy of moving parts will be converted into thermal energy. They are often used in industrial machinery and material-handling equipment to reduce the amount of friction between two moving objects. Thus, it reduces abrupt stops or prevents excessively high vibration amplitudes.
Friction dampers can be made from a variety of materials, from steel to urethane, as well as metals ( such as aluminium, stainless steel, brass and more).
A special feature of friction dampers is that they don’t wear out easily and are not affected by how fast the load moves or the surrounding temperature. These dampers are usually installed alongside structural bracing. One of the key advantages of friction dampers is their cost-effectiveness, making them a feasible option for Indian homes. They do not require maintenance. Friction dampers act as normal structural members under service loads and undertakes once the slip load is reached.
Tuned Mass Dampers (TMD)
A tuned mass damper helps to protect the building from vibrations. You can consider a TMD a giant pendulum that slows down, swaying as a building starts to vibrate.
This damper is often called a harmonic absorber. It is a mechanical vibration-dampening device designated for buildings and mass-mounted on one or more damped springs. This type of damper is commonly used in skyscrapers to protect buildings and occupants from strong winds and earthquakes. A Tuned Mass Damper (TMD) is typically made of 300 to 800 tonnes of steel and concrete. It helps reduce structural damage, prevent component failure, and minimize discomfort for the people inside.
Metallic Yield Dampers
Metallic dampers are renowned passive energy dissipation devices. They are commonly called yield dampers or metallic dampers and are commonly made of steel. They are made to undergo plastic deformation when a building vibrates during an earthquake.
You can reduce the structural response when subjected to wind and earthquake by installing metallic dampers into the buildings. After experiencing a strong earthquake, yield dampers typically will not revert to their previous configuration. Thus, you need to replace them. Metallic yield dampers are commonly used in Indian construction due to their simple installation and low maintenance requirements.
Viscoelastic Dampers
These viscoelastic dampers include an arrangement of steel plates between which viscoelastic materials are positioned. These dampers convert mechanical energy into heat. Its performance is based on the frequency of loading and the ambient temperature. Viscoelastic dampers are often used in small and medium-sized buildings.
Magnetic Dampers
Magnetic dampers are commonly called dynamic vibration absorbers. This is due to their exceptional ability to absorb dynamic vibrations. They are independent of temperature variations. This magnetic damper includes two racks, two pinions, a copper disk, and rare-earth magnets. Compared to other types, these dampers are quite economical.
How to Choose the Right Seismic Damper for Your Building?
When you are choosing a seismic damper from its various types, you need to consider the following major factors:
Building Height & Location (Seismic Zone):
The placement and type of dampers depend on the building’s height and seismic zone. As studied in research on optimal damper placement for tall structures by I. Brás and L. Guerreiro (2017), taller buildings typically require optimal placement of dampers to dissipate energy effectively. For instance, flexible frame structures benefit from lower-floor placements, while rigid wall-dominant buildings require dampers on upper floors. Additionally, optimal placement can reduce damping costs by up to 18% compared to uniform distribution.
In India, regions like the northeast are highly prone to earthquakes, making viscous dampers suitable for reinforced concrete buildings due to their proven efficiency in seismic retrofitting.
Budget (Compare Damper Costs):
Compare the cost of different seismic dampers and choose based on your requirements. Friction dampers are considered the most cost-effective option in India, and viscous dampers, while more expensive, are better suited for commercial structures.
IIT Delhi is working on developing yielding dampers as a low-cost alternative for mass adoption in India.
Maintenance Requirements:
Consider the maintenance requirements of the potential damper. Friction dampers require minimal maintenance, primarily regular painting to prevent corrosion, making them ideal for long-term use. Viscous dampers involve silicon-based fluids that may require periodic checks but provide superior energy absorption capabilities.
What are the Advantages of Seismic Dampers?
Seismic dampers offer several advantages. Some of them are:
- They can help to minimise the amount of damage that a building sustains during seismic activity.
- Seismic dampers can enable the durability of a building by reducing the amount of stress that is applied to the structure during an earthquake.
- They can help to enhance the safety of a building by minimising the risk of collapse or other failures.
What are the Limitations of Seismic Dampers?
- Seismic dampers offer considerable safety from a certain amount of shaking. Not complete safety. Once the damper has reached its maximum capacity, the building will be vulnerable to further damage.
- Seismic dampers require proper design and installation. Even a small mistake can induce the risk of damage to the building.
Top Indian Suppliers & Manufacturers of Seismic Dampers
Seismosys Technologies Pvt. Ltd. – Bengaluru, Karnataka: Known for manufacturing a wide range of seismic isolation and vibration control dampers, including viscous dampers.
VSL India offers advanced seismic protection systems, including seismic dampers.
KLA Const. Technologies Pvt. Ltd.: Tied up with Quaketek Inc. for friction dampers, enhancing earthquake resistance in structures.
Vigyashree Sharoda Infrastructure Ltd specialises in viscous hydraulic dampers in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
Cost of Seismic Dampers in India
Below are the estimated costs for various types of seismic dampers, which may vary depending on specific circumstances:
Viscous Dampers
Prices for spring viscous dampers can range from ₹15,000 per unit to ₹49,300 for models like the Dynemech Viscous Damper DVS-410-A.
Metallic Yield Dampers
Metallic yielding dampers are noted for being simple, cost-effective, and easy to fabricate. They are considered efficient due to their stable hysteresis, low cost, and ease of use.
Tuned Mass Dampers (TMD)
A Moog Tuned Mass Damper is listed at ₹3,000 per piece, while another source mentions a Tuned Mass Damper available for ₹3,499. The Tuned Mass Damper (TMD) market is valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach USD 2.4 billion by 2033.
Viscoelastic Dampers
An ARC viscoelastic damper for industrial use is priced at ₹8,000 per piece.
Magnetic Dampers
A magnetic shut-off damper is priced at ₹250,000 per piece. Wire tensioner magnetic dampers are available for ₹16,000 per piece. Electromagnetic dampers in vehicle suspension systems are listed at ₹5,962.
BIS standards for Seismic Dampers & Retrofitting
Building codes and guidelines are essential for the selection of seismic dampers. Ensuring that the chosen damper meets required safety and performance standards. The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) offers guidelines under IS 1893, which specify seismic design principles, including energy dissipation devices like viscous and ADAS dampers. These dampers mitigate seismic forces by reducing structural vibrations and preventing damage.
To make old buildings stronger with retrofitting strategies, BIS suggests methods like adding shear walls, steel braces, or base isolators. These methods improve the building’s side strength, flexibility, and stiffness. They are also cost-effective ways to make buildings safer and follow the latest earthquake safety rules. On a final note, seismic dampers can be used in both new buildings and retrofit projects. In new construction, they are typically installed between floors or within walls. For retrofit applications, they are often added to the roof or basement. It’s best to consult an expert or hire a professional construction company for proper installation.

