India is a country where humidity and temperature differ considerably. In urban areas, HVAC systems have become a great solution for maintaining indoor temperature for comfort and a healthy environment.
Read today’s Brick & Bolt blog to understand HVAC systems, their types, and maintenance in detail.
What is an HVAC System?
You can understand HVAC as a short form for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functions. This HVAC system controls the house’s indoor conditions with these functions. This system controls the room temperature through heating and cooling, and humidity levels by controlling air movement and distribution inside the room.
Key Components of HVAC Systems
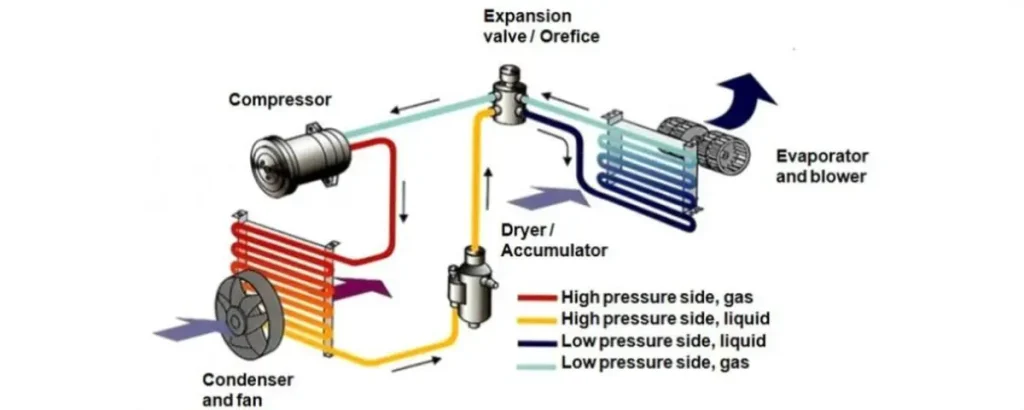
Image Source: Research Gate
An HVAC system is an essential part of comfort within the house. They are generally composed of:
Thermostat
This part is the control centre of the HVAC system. Thermostats regularly monitor the indoor temperature and adjust the HVAC system accordingly. It controls the indoor temperature by adjusting heating and cooling settings. If the temperature climbs above the set point, the thermostat activates the air conditioner to cool the space. On the other hand, if the temperature drops below the set point, the thermostat triggers the heating system to warm the area. This process will help to maintain a uniform and comfortable indoor climate while saving energy.
Furnace
A furnace is the main heating point. It provides warmth by heating air, later distributed within the house structure. A furnace will play a major role in maintaining a stable and comfortable indoor environment during colder months.
Condensing Unit
The condensing unit will be positioned outside the building. It will disperse heat absorbed from the indoor air and make the system cool. It will involve components such as the compressor and condenser coils, facilitating heat exchange.
Evaporator Coil
The HVAC evaporator coil is always placed in the indoor unit. It will absorb heat from warm indoor air. The evaporator coil absorbs heat from indoor air, facilitating the cooling process. HVAC evaporator coils will have evaporated refrigerant that cools the air and moves it to the coil.
Refrigerant Lines
Refrigerant lines are used to connect the indoor and outdoor units. This will enable the circulation of refrigerant that absorbs and releases heat during the cooling cycle. These insulated copper lines are an essential part of any cooling system. There are two types of refrigerant lines: liquid and gas. The liquid refrigerant line transports the coolant between the condenser and coils, while the gas refrigerant line carries the refrigerant gas.
Ductwork
Ductwork is responsible for circulating conditioned air throughout a building. It comprises supply and return ducts for efficient airflow and temperature control.
Air Filters
Air filters are essential for keeping indoor air quality by trapping dust, allergens, and other particles. Regular replacement of filters is required to ensure the efficient operation of HVAC systems and boost healthier air.
How do HVAC Systems Work?
The operational principle of HVAC systems depends on thermodynamics. It involves heating mode and cooling mode, which happen through controlled airflow.
- In heating mode, the system extracts cooler air from the indoor environment, which later passes through the heating unit. This air will be heated and distributed back into the living spaces through the blower fan. It will increase the overall temperature.
- In cooling mode, warm indoor air is drawn into the system and passes over the evaporator coils. Here, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, generating cooler air that will then be circulated throughout the spaces later.
- In the exhaust stage, stale air will be expelled from the building to maintain a fresh internal atmosphere.
In India, where humidity and temperature can vary significantly, HVAC systems must focus on temperature control and manage humidity levels effectively. Energy-efficient HVAC designs using inverter technology can adjust to varying loads, which is essential in climate-sensitive areas.
Types of HVAC Systems Based on Configuration
Whether you’re looking for heating and cooling solutions or exploring different air conditioning options, understanding the various HVAC system types is crucial.
Centralised HVAC Systems
A centralised HVAC system uses a central plant to control the temperature of a building. It distributes conditioned air or water through ducts or pipes to different areas of the house. This easy-to-maintain system will ensure consistent temperature and comfort. However, the installation costs of this system will be higher, and it is difficult to adjust to layout changes. These systems are mostly used in large buildings.
Ductless/Decentralized Systems
Ductless air conditioners have gained popularity for their flexibility. These mini-split systems offer independent temperature control for individual rooms, making them an attractive option for those seeking efficient heating and air conditioning. These ductless air conditioners do not use ducts to heat or cool a building. Rather, it uses smaller units that work independently in different areas. Mini-split systems have an outdoor compressor and indoor air handlers, providing heating and cooling without ducts. They allow each room to have its own temperature settings, making them energy-efficient and flexible. Window or wall units are small, self-contained air conditioners that fit into a window or wall. They are cheap and easy to install, but they are not powerful enough for large spaces. They can also be noisy and may not control temperature very accurately.
Hybrid HVAC Systems
Hybrid HVAC units offer the benefits of both centralised and decentralised technologies for higher efficiency. A common configuration incorporates a heat pump and a furnace. The heat pump is handled at moderate temperatures for effective cooling and heating. Significant temperature drops activate the furnace to generate warmth. This enhances energy efficiency and provides comfort for building occupants.
Geothermal HVAC
Geothermal HVAC makes use of energy stored in the earth to heat and cool your home. The earth’s surface is a natural heat gatherer. This heat is stored below the frost line and can be taken by using a pipe loop system and a heat pump. The loops are laid horizontally or vertically to absorb the heat from the ground. In these loops, a mixture of water and antifreeze circulates. The loops take the heated liquid to your home basement (where the heat pump is located). The heat pump extracts the heat from the liquid and moves it to your HVAC system, then distributes it throughout the house. After the heat is removed, the water circulates back into the loop system, repeating the process. That way, the free and renewable geothermal energy benefits heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Types of HVAC Systems in Detail Based on Application Area
Residential HVAC Systems
These HVAC systems are specifically designed for home and apartment requirements. These systems typically include smaller capacity units that are intended to serve typical residential spaces without extreme energy usage. Modern technologies, such as smart thermostats and energy-efficient designs, will improve comfort while controlling operating costs.
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems are designed to control the temperature of large spaces, such as larger office buildings and retail surroundings. They are more powerful and can control the temperature in different areas separately. This helps keep every part of the building comfortable based on how it is used and the number of people inside.
Industrial HVAC Systems
Industrial HVAC systems are strong and powerful heating, cooling, and ventilation systems designed for factories and large production areas. They help control temperature and air quality for manufacturing processes. These systems use special filters to keep the air clean, which is important in industries like medicine, food production, and aerospace. Industrial HVAC systems ensure that these places meet strict air and temperature standards.
Specialised HVAC Systems
Specialised HVAC systems are designed for places that need very precise temperature and air control. This systems help maintain strict air and temperature conditions in different industries.
- In clean rooms, the system keeps the air fresh by reducing dust and germs to protect products.
- Data centres need HVAC systems to keep computers cool and prevent them from overheating.
- Hospitals use special HVAC systems to keep the air clean and sterile for patient safety.
- Food storage areas also require proper temperature control to keep food fresh and safe.
Common HVAC Problems
HVAC systems can experience issues that can compromise their performance. Some of the common problems are:
Dirty Filters: This is one of the frequent issues. It can lead to reduced airflow and increased energy consumption. Regular filter changes are essential to prevent this problem.
Refrigerant Leaks: Low refrigerant levels can significantly affect cooling effectiveness and demand professional care to diagnose and repair properly.
Clogged Drain Lines: When condensate drain lines get blocked, water can back up and cause leaks, resulting in potential water damage.
Thermostat Problems: If thermostats don’t work properly, the HVAC system will not work efficiently. This will cause discomfort and uneven heating or cooling.
Electrical Issues: Electrical problems such as tripped circuit breakers or faulty wiring can disturb HVAC operation and require professional diagnostics.
Maintenance and Care of HVAC Systems
You need to maintain your house’s HVAC systems regularly. Regular HVAC cleaning will help maintain energy efficiency, prolong the system’s workability, and improve indoor air quality. Some routine maintenance tasks include changing air filters, cleaning coils, and checking refrigerant levels. These tasks will help to prevent costly breakdowns and major repairs by recognising potential issues early. Negligence in maintaining an HVAC system will cause reduced performance and increased wear and tear, which can lead to premature replacement.
The following are some DIY maintenance tips:
- Since clogged filters can limit airflow, change or clean air filters regularly, typically every one to three months, depending on usage and filter type.
- Keep the outdoor unit clean and free of debris. You can routinely remove leaves, dirt, and other obstructions around the unit to promote proper airflow and prevent damage.
- Make sure that vents are unobstructed for balanced airflow throughout the home.
- Check condensate drain lines for leaks and clear blockages. Regularly inspecting these lines and using a vinegar solution to prevent algae buildup can help avoid water damage and maintain system performance.
When Can You Repair and Replace HVAC Systems?
Depending on the age of the system, the cost it takes to repair will help you decide whether to repair it or replace it with a new one. A common thumb rule is to consider a replacement if the cumulative repair costs exceed 50% of the cost of a new unit. Also, if the HVAC system is older than ten years and frequently requires repairs, replacement may be the better choice.
Without any doubt, HVAC systems maintain indoor climates, providing manageable heat, air cooling, and ventilation based on the particular environment. HVAC will be opted for energy efficiency. Regular HVAC cleaning and care will help to maintain their efficiency, longevity, and reliability. Regular maintenance also helps to avoid costly repairs and replacements. You have to recognise the variety of HVAC systems and their classifications to select the solutions that are suitable for your house needs.

