Steel mesh is among the most crucial materials in contemporary construction and industrial use. This strong, durable, flexible product is used for a multitude of functions within different industries. From reinforcing concrete to making security screens, steel mesh is dependable in its performance for challenging environments. Its grid structure, developed through various manufacturing processes, leaves spaces of different sizes and shapes based on particular demands.
Steel properties, usage, and production processes are learned to enable specialists to make the right choices for their projects and provide maximal performance in a wide range of applications.
What is Steel Mesh?
Steel mesh is a fabricated product formed from interlocked steel wires that are kept in a regular grid. The arrangement allows for equal openings throughout the frame, enabling the control of air, light, or materials while providing structural stability.
The mesh attains strength at the points of intersection where wires meet one another, forming a strong network that distributes load evenly across the surface. Steel mesh is, thus, one of the very basic materials in almost every application that needs a balance between permeability and structural strength; hence, it finds ample use in the fields of construction, industry, and commerce.
Properties of Steel Mesh
- Strength
Steel mesh has long been recognised as a material with an exceptionally high degree of strength, making it an excellent choice for construction, reinforcement, and industrial purposes. The woven or welded pattern ensures that the steel mesh has the highest tensile strength, meaning it is capable of withstanding loads of weight and force without any structural failure.
- Durability
The steel mesh has the durability to enable it to survive under critical environmental conditions, such as high pressure and extreme temperatures. This reliability ensures the product’s long life support, and even applications facing challenges like mining, construction, and outdoor environments can be performed without shortening the lifetime of steel mesh.
- Corrosion Resistance
The high chromium content, at 16% or even higher, present in stainless steel mesh, helps it to be highly resistant to corrosion. Stainless steel mesh is the right material selection for environments that primarily face factors such as moisture, acids, or alkalis. The capability to resist the impact of Steel rust is an added advantage of steel mesh, and it will, thus, have a long lifespan with minimal wear, even when used in outdoor or industrial settings.
- Flexibility
Steel mesh is highly flexible, allowing it to be shaped in various ways while retaining its strength. It is this characteristic that makes it usable in multiple applications, such as the creation of custom enclosures and structures that require reinforcement.
- Cost-Effectiveness
Steel mesh is a cost-effective alternative for anyone looking to make savings, as it requires minimal maintenance and is of high quality for long-term use, with no need for repairs or replacements.
Application of Steel Mesh

Steel mesh is a versatile material used in a wide range of sectors for different kinds of applications.
1. Common Use
- Fencing & Security: Steel mesh is the go-to material for security barriers and fencing owing to its sturdy and robust nature. It is quite a common solution for residential, commercial, and industrial fencing.
- Architectural Design: Steel mesh is incorporated into the design of modern architecture for both aesthetic and functional purposes, such as facades, panels, and interior partitions that are designed to seamlessly integrate with their intended function.
2. Construction Use
- Reinforcement of Concrete: Steel mesh plays an irreplaceable role in the full reinforcement process of concrete, thereby increasing strength and reducing the number of cracks in the construction. The most common application is in building, road, and bridge construction.
- Supporting Concrete Slabs: This is one of the main applications where steel mesh is used. It is thus used to carry the full load of the slab, providing extra durability and the ability to support more weight.
3. Industry Use
- Filtration & Sieving: Steel mesh is utilised in the filtration process, particularly in the separation of solids and water in the water processing and mining industries, where the mesh size is crucial for the liquid-solid separation process and the purification of the product.
- Material Handling: This mesh is used not only for its structural strength but also for transporting raw materials from one location to another. For example, in a factory, it levels out many processes in material storage and movement.
Principal of Steel Mesh
Steel mesh relies on basic engineering principles that optimize structural efficiency through geometric optimization. The grid pattern of applied loads is spread along numerous intersection points, avoiding failure concentration at isolated points. Wire intersection angles determine the flexibility and strength properties of the mesh, with right-angle configurations providing the best rigidity.
Opening size influences permeability and structural performance, and balance is needed between functional demand and mechanical characteristics. Load transmission mechanisms utilise the interconnected wire network to distribute forces uniformly throughout the mesh structure. Such principles provide consistent performance while minimizing material use and process efficiency.
Types of Steel Mesh
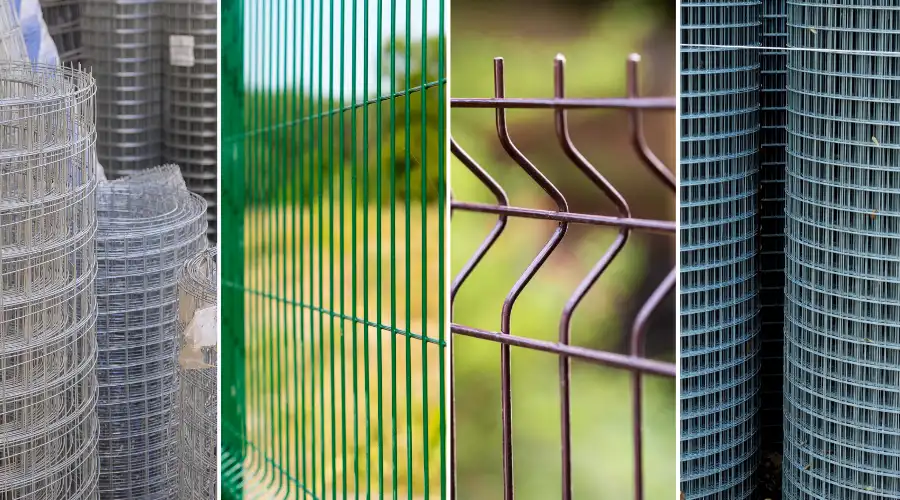

Welded Steel Mesh
Welded steel mesh is developed by welding single wires together at crossover points with heat and pressure. Steel mesh forms strong and stable frameworks that can carry heavy loads with ease. The welding ensures permanent unions that cannot be separated when subjected to stress.
Woven Steel Mesh
Wires are crossed over and beneath each other in a regular pattern to form a woven mesh. The method yields flexible meshes that can adapt to curved surfaces without compromising structure. The process of weaving makes it possible to have accurate control over opening sizes.
Expanded Steel Mesh
Expanded steel mesh starts with solid sheets of steel that are subjected to cutting and stretching operations. This production process creates diamond-shaped openings along with material continuity. The mesh produced possesses superior strength-to-weight ratios and better load distribution characteristics.
Stainless Steel Mesh
Chromium and nickel, which are found in stainless steel mesh, shield it from rust, damage, and high temperatures. Various grades have different properties, with Type 304 used in general applications, Type 316 is corrosion resistant steel, and Type 430 with magnetic properties.
Galvanized Steel Mesh
Galvanized steel mesh has a zinc coating on the underlying steel materials. The protective coating stops corrosion and prolongs service life in outdoor applications. The process of galvanization produces a barrier that protects underlying steel against weather conditions.
Key Benefits of Steel Mesh
Steel mesh has many benefits that make it better than other materials, as follows,
- Very high tensile yet not heavy– Steel mesh does not tend to bulk; hence, it fulfils the basic requirements with lesser material.
- Rust resistance– Stainless and galvanized type of steel rarely rust; hence, they last longer, especially in harsh weather and damp locations.
- Can be customized– Wire thickness, hole dimensions, and mesh shapes may be selected based on project requirements.
- Cost-saving for the future– It is durable and requires less repair and maintenance, thus reducing long-term expenses.
Manufacturing Process of Steel Mesh
Wire Drawing
Wire drawing decreases the rod diameters of steel using progressive dies to produce evenly sized wire dimensions. Work-hardening makes the material, which enhances tensile strength without compromising ductility. Quality checks ensure the mesh is made to the correct size and strength, with a good surface finish for longer-lasting coatings.
Mesh Formation
Mesh formation constructs wire arrangements in predetermined patterns and welds or weaves them together. Proper spacing and positioning are achieved with automation equipment. Inspections make sure the steel mesh follows all the needed quality rules and guidelines.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment applies protective coatings such as galvanization or powder coating to enhance corrosion resistance. Treatment selection depends on intended application and environmental exposure conditions. Good surface cleaning helps the coating stick well and last longer.
Quality Control
Quality control procedures verify mesh dimensions, wire properties, and joint structural integrity through standardized testing methods. Regular checks make sure the mesh follows all safety and quality rules. Documentation maintains traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
Finishing Operations
Finishing operations are cutting to size, edge treatment, and packaging for shipment. Custom-made mesh is created for projects with special needs or setups. Final inspection ensures product quality prior to delivery to customers.
Considerations in Designing Steel Mesh
Environmental Design Considerations
Environmental considerations heavily impact mesh choice and design criteria. Corrosive environments demand proper material grade and protective coatings. Extreme temperatures influence material properties and dimensional stability. Moisture exposure demands corrosion-resistant materials and effective drainage design.
Load Requirements
Load requirements are what drive wire diameter, spacing, and support structure design. Static loads demand different consideration than impact or dynamic loading conditions. Safety factors ensure sufficient performance under maximum anticipated loads without causing catastrophic failure.
Opening Size Selection
Opening size selection strikes a balance between functional requirements and structural performance requirements. Security applications demand small openings to resist intrusion while still providing visibility. Filtration applications call for specific opening dimensions to realize desired separation characteristics.
Installation Methods
Installation techniques impact mesh design details like edge treatment, mounting provisions, and tolerances of dimensions. Conditions in the field determine installation difficulty and support structure needs. Accurate installation guarantees maximum performance and service life.
Requirements for Maintenance
Maintenance needs differ as a function of material used, exposure to the environment, and application stresses. Accessible designs promote inspection and cleaning activities. Schedules for preventive maintenance prolong service life and uphold performance standards during periods of operation.
Conclusion
Steel mesh is a vital material in contemporary building and industrial use, with unparalleled versatility and performance attributes. Its array of types, ranging from welded to expanded forms, offers solutions for innumerable uses across diverse industries. Knowledge of these technical features allows intelligent decision-making and the best project results.
For your next building project that needs trustworthy steel mesh solutions, think of collaborating with Brick & Bolt company, where professionalism intersects with excellence to provide quality output that lasts forever.