Glass is one of the oldest materials used in building projects. With advancements in material technology, many different types of glass have been developed, marking a shift in building practices. Various types of glass in construction industry across the world are widely used today, each with unique properties and purposes. Keep reading to understand the basis on which classification of glass is done, different types of glass used in building construction and their properties and applications.
Glass in Construction
Glass as a construction material is known for its distinct properties, of which the main one is its complete transparency. This transparency helps create innovative and sleek facades in modern architecture, apart from maximising natural light in enclosed areas. However, new developments have led to enhanced/ modified properties—including strength, transparency and finish—in building glass, leading to the availability of several glass types and uses. Some of the commonly used glass types in construction are as follows:
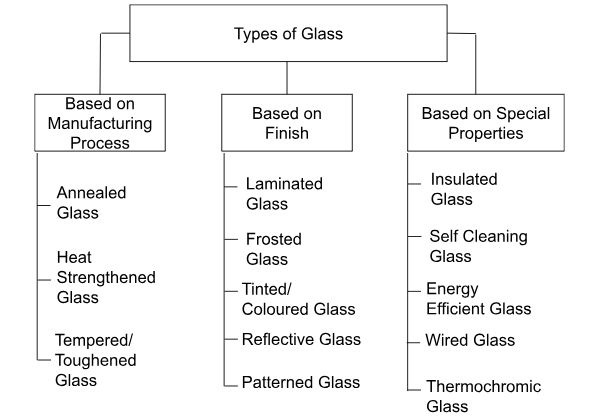
Types of Glass Based on Manufacturing Process
Annealed Glass
The most basic glass kind made during production is annealed glass, often known as float glass or flat glass. It is made by the ‘float glass process’, which involves letting the molten glass cool very gradually until it reaches room temperature and gains sufficient strength without breaking. Since it is not very strong, it is used to make types of windows and doors that do not require too much security and for furniture and interior products (such as display units and shelves). Annealed glass is also used to make glass varieties with stronger and more sophisticated qualities.
Heat-Strengthened Glass
After being heated to a temperature of approximately 600°C to 700°C, annealed glass is rapidly cooled. The mechanical and thermal strength of glass produced by this reheating and rapid cooling technique is double that of annealed glass. Heat-strengthened glass is used for external doors, windows, and other areas that need more strength than regular glass, but it cannot be used for structural applications. It is also used for making curtain walls and staircase components like frameless glass railings and balustrades.
Tempered Glass/ Toughened Glass
When annealed glass is reheated to a temperature of 600°C to 700°C, toughened glass or tempered glass can also be produced. However, the cooling process here is much faster and involves treating the glass to blasts of air. Compared to annealed glass, tempered glass is four to five times stronger and suitable for structural use in contemporary glass buildings. It is commonly used to make skylights and other glazing types for roofs, shower enclosures and internal partitions.
Glass Kinds Based on Finish
Frosted Glass
Frosted glass is made by the process of sandblasting or acid etching. Sandblasting involves subjecting normal glass to a pressured blast of sand or other such abrasive materials. In acid etching, normal glass is treated with hydrofluoric acid, which corrodes glass and gives it a frosty finish. Such glass is ideal when privacy, regulated amounts of light transmission and/ or decorative finishes are required in a space. These include bathrooms, shower enclosures, accent features and interior partitions.
Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is made by adding a core laminate layer between two sheets of annealed, heat-strengthened or toughened glass. These layers are then joined with heat and/or pressure. The core layer is generally made of Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB), which is a type of plastic material in the form of a sheet 1-2mm thick. Such glass offers higher strength, better insulation and shatter-resistance. Laminated tempered glass is used to create structural glazing, floors, roofs and partitions.
Tinted Glass/ Coloured Glass
Tinted or coloured glass is produced by adding metal oxides to the molten glass mix during manufacture. The type of metal oxide added depends on the colour required. For example, oxides of chromium are added to obtain a green colour, cobalt for blue and selenium for red. Coloured or tinted glass is used to enhance the energy efficiency and aesthetics of different glass products or to increase privacy, especially in facade design and interior design.
Reflective Glass
Reflective glass or mirror glass is made by applying a metal oxide coating to the glass mix while it is still hot during the manufacturing process. This type of glass in construction has a better resistance to scratches, weathering and fading. It is one of the commonly used types of window glass in green buildings and zero energy buildings, as it helps reflect light and create more energy-efficient spaces. However, reflective glass is most frequently used to make mirrors for use in interior spaces.
Patterned Glass
Patterned glass is produced by embossing, moulding or engraving glass with the required designs while it is still hot. Various types of glass patterns are available today, such as fluted, reeded, stained and etched. All types of glass patterns are made by passing molten glass through rollers with the desired designs. Patterned glass is typically used for decorative purposes in interior spaces.
Glass Varieties With Special Properties
Oftentimes, the natural properties of glass are modified to suit specific requirements in modern construction. A few common types of glass used in construction after modifying or enhancing their properties are:
Insulated Glass
Two or more glass panels are joined together with a spacer and sealant to form insulated glass. The space between the glass panes is filled with air or inert gases. This type of glass in building construction is mainly used on exterior facades to increase energy efficiency, as it can extend the time taken for heat transfer between spaces, thus ensuring effective building insulation.
Self-Cleaning Glass
During the manufacturing process of this type of glass, a coating of titanium oxide is applied to float glass. This coating can decompose any organic dust particles under the action of UV rays in sunlight. It also facilitates the clean flow of water along its surface, thus ensuring that no dirt or stains accumulate on its surface. Such types of tempered glass are especially beneficial for use as facade elements in skyscrapers, where cleaning can be a difficult process.
Energy Efficient Glass/ Low-E Glass
Low Emissivity or low-E glass has an ultra-thin coating of metal (generally tin or silver) oxide. This coating blocks the passage of harmful long-wavelength rays (such as UV and infrared), while allowing short-wavelength light to pass through it. Thus, this advanced technology can ensure regulated daylight conditions indoors with almost any building orientation, forming an important component of climate responsive architecture.
Thermochromic Glass
Thermochromic glass has a chemical coating (typically vanadium oxide) or laminate layer which helps it change its colour and/or opacity under light. Also known as photochromic or smart glass, this type of glass turns dark when it is exposed to natural light or UV rays. Such glass facades can be integrated with building automation systems to ensure year-round thermal comfort indoors.
Wired Glass
A metal (generally mild steel) mesh is sandwiched between two layers of glass to produce wired glass. This glass variety has a much higher resistance to cracks, shattering and fires. It is typically used in fire exit doors and windows near fire escape pathways, where it can prevent fires from spreading too quickly across a building. Although not as strong as laminated or toughened glass, it is used to enhance security in openings.
Glass Types and Uses in Construction
The following is a summary of the above mentioned glass types and their common uses in construction:
| Type of Glass | Common Applications |
| Annealed glass | Doors, windows and interior partitions with low strength. Also used to make other stronger varieties of glass. |
| Heat strengthened glass | External doors, windows, curtain walls, railings, balustrades, etc. |
| Toughened glass | Skylights, glass roofs, structural glazing, staircases and facades. |
| Frosted glass | Bathrooms, shower enclosures, interior partitions, privacy doors. |
| Laminated glass | Structural glazing, floors, roofs, safety doors and windows. |
| Tinted/ coloured glass | Facades, interior partitions, doors, furniture and interior decor. |
| Reflective glass | Office/ store front doors, windows and facades. |
| Patterned glass | Bathrooms, shower enclosures, interior partitions, privacy doors, furniture and interior decor. |
| Insulated glass | External doors, windows and other openings in regions that require higher levels of temperature control indoors. |
| Self cleaning glass | Facades, doors and windows of tall buildings and skyscrapers. |
| Energy efficient glass | Facades of zero-energy or sustainable buildings. |
| Thermochromic glass | Exterior facades of large-scale low-energy commercial and residential buildings. |
| Wired glass | Fire-rated or high-strength doors, windows and other openings. |
Using the Best Types of Glass in Construction Projects
With the use of glass in construction typically being vital, different varieties of glass can be found in most building projects. Brick & Bolt, a leader in the construction industry, offers top-quality building materials supply in India to streamline construction processes. The company also provides design-build services for residential and commercial projects across multiple cities in India. Backed by skilled design and expert execution, the company has 7000+ completed projects, cementing itself as a trustworthy organisation. To ensure that the best types of glass in construction are used in your building project, reach out to Brick & Bolt today!

