Bricks are an important construction material that has been used for centuries, as they play an important role in the development of architecture and infrastructure. Many people are often confused before the construction of civil structures like buildings or houses about whether to use red bricks or cement blocks as the construction material. Everyone wants the construction to be durable and safe, considering it a one-time process that cannot be reversed.
So understanding the differences between red bricks and cement bricks can be advantageous for making an effective decision before construction. This blog helps in exploring the details regarding the cement bricks and red bricks.
Cement Bricks
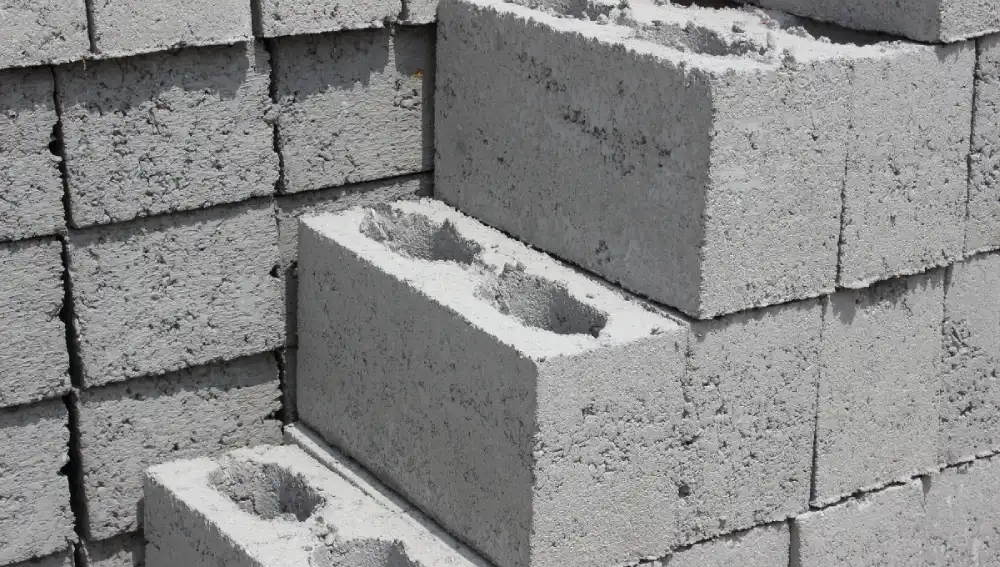

Cement bricks are also called concrete bricks, and they are produced by using a combination of cement, fly ash, sand, and water. Here cement will act as a binding agent, while sand provides strength and reduces the amount of cement needed. Fly ash is a by-product of coal combustion that helps improve strength and durability, while water is necessary for the chemical reaction to take place between the cement and other materials.
Cement bricks are made by various steps, including mixing, molding, and curing. The types of cement bricks include,
- Solid blocks
- Hollow blocks
- Fly ash bricks
The hardening of cement bricks occurs with the help of sand concrete and aggregate like gravel, slag, crushed stones, etc., as the result of a chemical reaction. With the correct ratio of inputs, cement bricks can be produced more efficiently and have high resistance to different environmental conditions and external factors.
Red Bricks
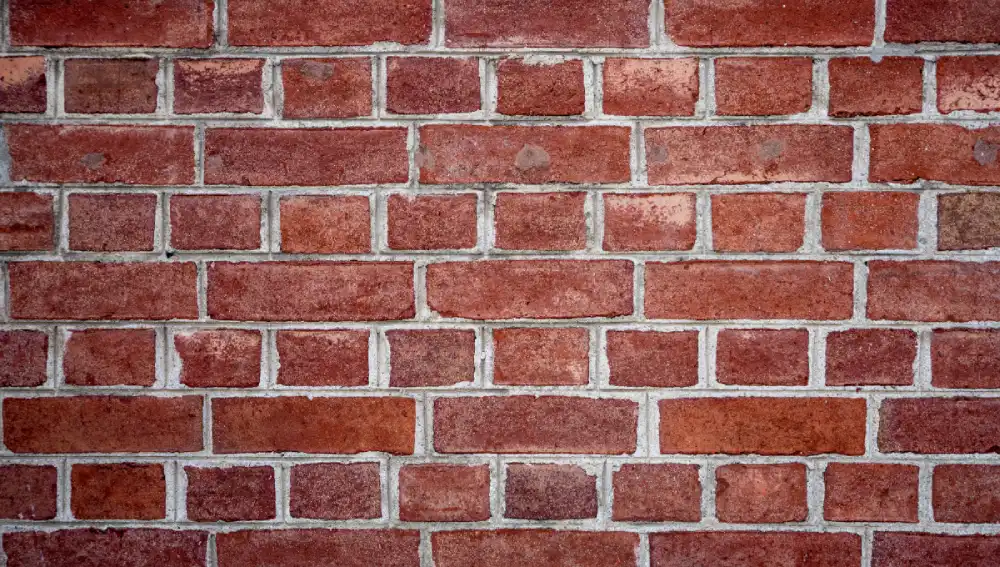
Red bricks are also called clay bricks, are one of the oldest building materials. They are mainly made from clay, sand, and water. Here, clay is the primary material that gives plasticity and strength, while sand is used to temper the clay, and it prevents excessive shrinkage during the drying process. Water is important for molding the bricks and getting the correct consistency.
The main steps involved in the production of red bricks are molding, drying, and firing. There are various types of redbrick, and some of them are,
- Traditional red bricks
- Refractory bricks
- Engineering bricks
Red bricks are usually made by burning or baking a mixture of clay, soil, and water in a kiln. The output from this process gives durable, fire-resistant bricks that exhibit seismic and insect resistance properties.
Availability of Grades and Types
Red Bricks
Red bricks are readily available in various sizes and quantities locally. They come in different grades and types, each varying in strength and specific applications.
Grades
- First Class: These bricks are well-burnt and have a uniform shape. Suitable for flooring and constructing permanent structures like arches, external walls, and reinforced brickwork. It will have a minimum compressive strength of 10 N/mm².
- Second Class: Commonly used for interior tasks such as building compound walls, and partition walls, but not for flooring. It will have a compressive strength of approximately 7.5 N/mm²
- Third Class: These bricks are overburnt, often have a rough texture, and may have irregular shapes. They are ideal for temporary structures and pavements. Generally, it will have a compressive strength of around 3.5 N/mm² (or 35 kg/cm²) to 5 N/mm² (50 kg/cm²), depending on specific classifications.
- Fourth Class: Usually called Jhama bricks. Includes Zhamas (over-burnt) and Pilas (half-burnt), typically used as aggregates in road construction, foundations, and floors due to their lower strength. It will have a minimum compressive strength of about 1.5 N/mm² (or 15 kg/cm²).
Cement Bricks
Cement bricks are also available locally in various sizes and quantities. They are in different grades and types.
Grades
- Grade A: This has the capacity to withstand heavy loads, with a minimum block density of 1500 kg/m³. Grade A bricks are the top-tier option, specifically engineered to withstand heavy loads. These bricks are suitable for constructing high-rise buildings, industrial structures, or any project that requires a robust and durable foundation. They provide superior strength and stability, making them a reliable choice for critical structural elements.
- Grade B: Suitable for medium-loads to heavy loads, and they have block densities that range from 1100 kg/m³ to 1500 kg/m³. Grade B cement bricks are designed for projects that require medium to heavy load-bearing capacity. These bricks are suitable for a variety of construction tasks like walls, partitions, and general masonry work. They provide a balance between strength and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for both residential and commercial buildings.
- Grade C: Commonly known as solid concrete blocks. They have a minimum block density of 1800 kg/m³. Grade C cement bricks are known for their high density and durability. These bricks are suitable for constructing load-bearing walls, foundations, and other components that needs a solid and reliable base. Grade C bricks are often used in applications where maximum strength and minimal porosity are essential, ensuring long-lasting performance even under challenging conditions.
Types
- Solid concrete blocks: These are mainly used for the construction of load-bearing structures. Their high density and strength make them suitable for supporting significant weights like foundations and walls of buildings. These blocks are known for their excellent fire resistance and sound insulation properties, contributing to the safety and comfort of a building.
- Hollow concrete blocks: These are mainly used for the construction of load-bearing exterior and interior walls. Hollow concrete blocks are designed with hollow cores, reducing the overall weight of the block while still providing structural integrity. The hollow cores can be filled with insulation materials or additional concrete to improve the thermal and acoustic insulation, making them an option in modern construction.
- ACC blocks (Autoclaved Aerated Concrete blocks): ACC blocks are a lightweight and innovative alternative to traditional bricks and concrete blocks. These blocks are made from a mixture of cement, lime, sand, water, and an expansion agent that creates air pockets within the block. This makes the block both strong and lightweight, making it easier to handle and reducing the overall load on the structure. ACC blocks are also known for their excellent thermal insulation properties, which can contribute to energy efficiency in buildings.
- Paver blocks: They are used for making sidewalks, petrol bunk floors, driveways, etc. These blocks are available in a variety of shapes, colors, and patterns, allowing for creative design solutions in landscaping and outdoor spaces. Paver blocks are highly durable, resistant to wear and tear, and can withstand heavy traffic, making them a practical choice for both residential and commercial projects.
Differences Between Cement Bricks and Red Bricks
| Feature | Cement Bricks | Red Bricks |
| Strength and Durability | Higher compressive strength, enhanced durability. | Lower compressive strength, more prone to weathering. |
| Thermal Insulation | Less effective thermal insulation. | Provides better thermal insulation, absorbs and releases heat. |
| Water Absorption and Resistance | Lower water absorption, less risk of dampness. | Higher water absorption, can be treated for better resistance. |
| Weight and Density | Denser and heavier, contributing to strength but increasing structural weight. | Lighter, easier to handle, reduces foundation load. |
| Cost and Availability | More cost-effective, uniform quality, widely available. | Often more expensive, labour-intensive manufacturing and is regionally available. |
| Environmental Impact | More sustainable, uses by-products like fly ash, lower carbon footprint. | Significant environmental concerns, deplete topsoil, high energy consumption. |
| Recycling and Reusability | Easier to recycle, can be reused in various forms. | Can be recycled, but the process is more labour-intensive. |
| Applications and Suitability | Ideal for load-bearing structures, modern construction techniques. | Preferred for aesthetic and historical projects, residential buildings. |
Cost of Bricks
The cost of red bricks in the market is generally low and affordable, with prices ranging from ₹7 to ₹25 per brick, depending on various factors such as dimensions and quality. In different regions, such as Bengaluru, the prices can specifically range from ₹8 to ₹10 per brick. If we consider the overall requirement during the construction process, then the demand for mortar mix and repairs, if necessary, may make the overall cost higher.
The cost of cement bricks varies widely across different cities, typically ranging from ₹27 to ₹45 per brick. For example, in Bengaluru, cement bricks cost approximately ₹28 to ₹34 each, while in NCR-Delhi, they can go up to ₹36 to ₹45 per brick . As the cement bricks need less mortar mix they can be repaired easily. The number of cement bricks used in construction is similar to that of red bricks, which balances out the total cost aspect.
Conclusion
When comparing the red bricks and cement bricks, we can understand their strengths and weaknesses clearly. Cement bricks have high strength, durability, and environmental benefits that make them suitable for construction projects that have high low bearing capacity. The red bricks will give excellent thermal insulation and aesthetic look, so they can be used in residential buildings and restoration projects.
FAQs
Cement bricks have lower water absorption compared to red bricks.
Cement bricks contribute to a lower carbon footprint compared to red bricks.
Red bricks are better suited for historical restorations due to their traditional material composition.
Yes, red bricks offer some resistance to seismic activities due to their natural material properties.
Yes, cement bricks, like paver blocks, are commonly used in sidewalks and pavements.

