A foundation is a construction structure that helps support a building and transfers its weight to the earth. It acts as the stabilizing anchor to keep things from settling or collapsing. Additionally, several foundations depend on the soil, climate, and general structure design.
India has a vast range of soil types, from sandy ground in some areas to clayey soil in others. When determining the best foundation for them, one should consider elements like earthquake-prone locations. It’s crucial to remember that in earthquake-prone areas, a thorough seismic analysis and design of a subset of structural analysis that calculates how a building or nonbuilding structure will respond to an earthquake should be carried out by qualified structural engineers to make sure the foundation type selected satisfies the site’s unique requirements and local building codes. A well-designed and sufficiently strong foundation is required for long-lasting, secure homes in India.
Different Types of Foundations Used in Construction in India

In India, various types of foundations are used in construction, and the choice depends on factors such as soil conditions, building requirements, and local regulations. There are mainly two types of foundations used in India for house construction.
- Shallow Foundation
- Deep Foundation
1. What is the Shallow Foundation
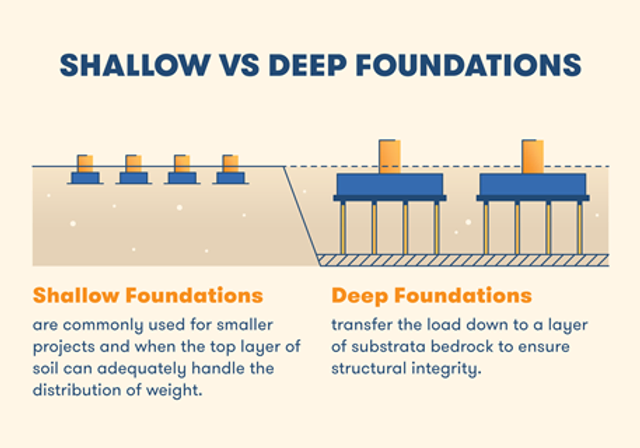
A shallow foundation transfers a building’s weight to the Earth extremely close to the surface instead of deeper soil or rock layers. Low-rise buildings and smaller, more superficial structures like houses typically employ these foundations. It provides stability without requiring much excavation by distributing a building’s weight across a wider region near the surface.
Shallow foundations are constructed where the soil can adequately support the structure without deep excavation. The soil type, seismic activity, and project needs affect their suitability. Technical assessments and structural reports are essential for determining which foundation is best for building houses in India.
Types of Shallow Foundations
There are five types of shallow foundations and they include
- Individual /Isolated Footings
- Combined Footings
- Raft or Mat Foundations
- Strip Foundations
- Slab-on-Grade Foundations
2. What is Deep Foundations
Deep foundations are the type of foundations that transmit the load of the structure further down the earth in comparison to shallow foundations. Typically, the depth-to-width ratio of this foundation exceeds 4 to 5. In practical terms, if the width of the foundation is W, the depth would be at least 4 to 5 times that value, creating a foundation that is deeper in the ground compared to its horizontal dimensions. Deep foundations often use this design consideration to enhance their load-bearing capacity and overall performance. These foundations are employed when shallow foundations are impractical due to inadequate soil strength or when the construction project requires support at considerable depths.
Types of Deep Foundations
Five types of deep foundations are generally used in home construction. They include:
- Pile Foundations
- Well Foundation
- Basement Foundation
- Buoyancy Raft
- Shaft Foundations
Difference Between Shallow and Deep Foundation
Selecting the appropriate foundation is a crucial choice that every homeowner would make, as it will impact the outcome, quality, and overall satisfaction of your project.
This comparison below aims to clarify how to decide which foundation is better. We seek to present a thorough analysis of shallow and deep foundations, a more dependable and innovative solution for your house construction.
| Basis | Deep Foundation | Shallow Foundation |
| Depth | The depth of a deep foundation is a critical aspect of civil engineering and construction, where the primary goal is to ensure the stability and structural integrity of buildings and infrastructure. Deep foundations are designed to transfer loads from a structure to deeper, more stable layers of soil or bedrock. | When designing and constructing buildings and other structures, the depth of a shallow foundation is a crucial consideration. A shallow foundation is placed near the earth’s surface or at a short depth below where the structure will be built. Its purpose is to evenly disperse a building’s or structure’s weight onto the ground near the surface, unlike deep foundations, which bury themselves deeply into the ground or bedrock. |
| Types | Deep Foundations include different types such as Caissons, Piles, Basement, Buoyancy Rafts and Shaft Foundations. | Deep Foundations include different types such as Caissons, Piles, Basement, Buoyancy Rafts, and Shaft Foundations. |
| Suitable Conditions | Perfect for applications requiring a higher load-bearing capacity, expansive clay, or weak or compressible surface soils. | Shallow foundations are ideal for projects involving hard and stable soil nearer the surface. |
| Construction Process | Deep Foundations include different types such as Caissons, Piles, Basement, Buoyancy Rafts, and Shaft Foundations. | Involves digging a shallow trench and laying footings made of reinforced concrete directly on the unaltered soil. |
| Advantages | The Deep foundation enhances load-bearing capacity, lowers settling risk, and works well with various soil types. Ideal for providing stability for large buildings. | Shallow foundations are more affordable for lightweight constructions, accessible to assemble, and appropriate for stable soil types. Frequently employed for modest residential constructions. |
Factors Affecting the Selection of Foundation
Choosing the proper foundation depends on some decision-making factors, including soil analysis, project load requirements, cost considerations, environmental impact, structural design, regulatory approval, and expert consultation.
Soil Analysis:
To comprehend the soil profile, bearing capacity, and possible settlement, do a thorough soil testing. Having this knowledge is essential for choosing the right type of foundation.
Project Load Requirements:
Analyze the loads the structure is expected to support. A deep foundation could be more suitable for large constructions or difficult soil conditions.
Cost Considerations:
Compare the financial effects of shallow and deep foundations, considering the price of materials, laborers and machinery requirement, the time requirement for building, and excavation.
Environmental Impact:
Evaluate how each type of foundation will affect the environment, considering excavation, site disturbance, and construction-related activities.
Structural Design:
Consider the structural design requirements of the project. The type and amount of loads and the overall design can influence the choice between deep and shallow foundations.
Regulatory Approval:
Check the local building codes and regulations to ensure the foundation standards are met. Specific regulations may influence the decision between shallow and deep foundations in some areas.
Expert Consultation:
Consult geotechnical engineers and foundation professionals for expert advice and recommendations tailored to your construction site’s unique circumstances.
Shallow Foundation and Deep Foundation Diagram
Conclusion
the decision between deep and shallow foundations depends on many factors, such as the properties of the soil, the structure’s load requirements, the surrounding environment, and financial limitations. Shallow foundations are less expensive and easier to build; they are recommended for constructions where the soil close to the surface has the bearing capacity to support the weight. They work best in lighter and smaller buildings. On the other hand, deep foundations are required when the surface soils are weak or have other constraints preventing them from bearing the structure’s weight. They are appropriate for large, heavy constructions or locations with difficult soil conditions because they extend farther into the ground to disperse the load to more stable soil or rock layers.
The choice of foundation type should be made after carefully examining the site’s characteristics, structural needs, and finances. Each foundation type has benefits and application areas. Whether a shallow or deep foundation supports a structure, the ultimate objective is to guarantee its lifespan, stability, and safety. Cooperation with geotechnical engineers and foundation professionals is essential to guarantee a dependable and practical foundation that satisfies the unique requirements of your building project.

